Ksama Arora
Build a Pipeline
Define pipeline by creating a YAML file or use function @pipeline() function to create YAML file. PythonScriptStep is the pipeline step used to perform tasks in a sequence, such as one step that prepares input data and a following step that trains a model
IMP NOTE: To pass data between two pipeline using Python SDK
from azureml.data import OutputFileDatasetConfig from azureml.pipeline.steps import PythonScriptStep prepped_data = OutputFileDatasetConfig('prepped') # Prepare Data Step step1 = PythonScriptStep( name="Prepare Data", script_name='data_prep.py', arguments=['--out_folder', prepped_data] ) # Train the model step2 = PythonScriptStep( name="Train Model", script_name='data_prep.py', arguments=['--training-data', prepped_data.as_input()] )
Step 1: Prepare data and Train model
from azure.ai.ml.dsl import pipeline
# Define the pipeline function
# The pipeline function expects pipeline_job_input as the overall pipeline input.
@pipeline()
def pipeline_function_name(pipeline_job_input):
# First pipeline step: prepare data
# The first pipeline step requires a value for the input parameter input_data, which is provided by pipeline_job_input.
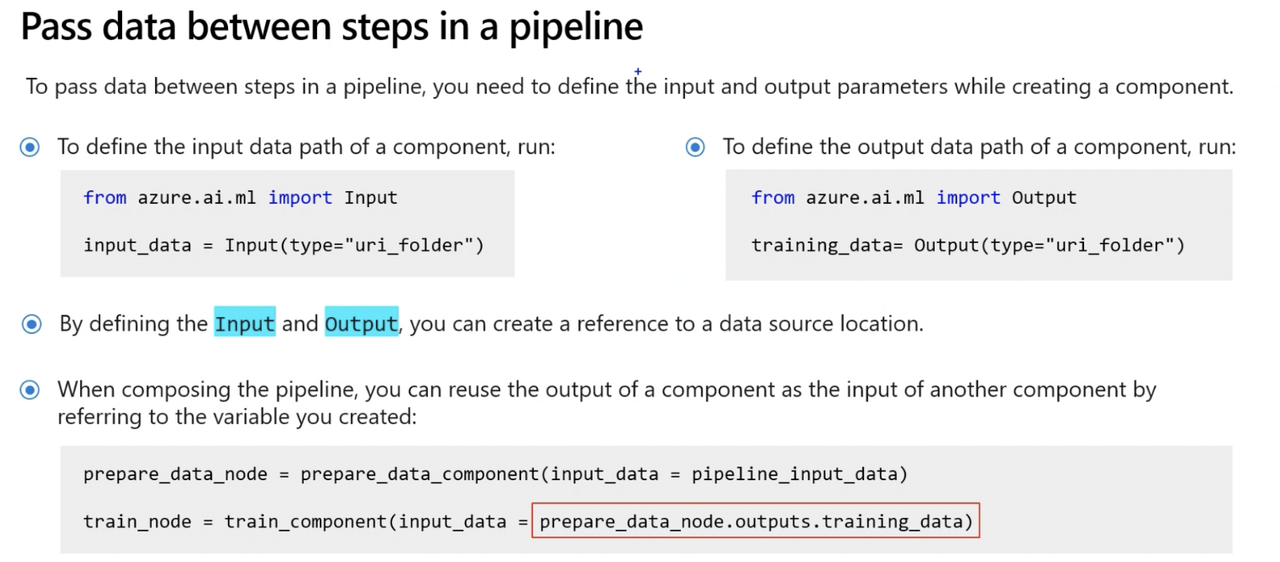
prep_data = loaded_component_prep(input_data=pipeline_job_input)
# Second pipeline step: train model
# The output of the first step is used as the input for the second step.
# The second pipeline step is defined by the loaded component for train_model and results in a trained model referred to by model_output.
train_model = loaded_component_train(training_data=prep_data.outputs.output_data)
# Define pipeline outputs
# Output 1: pipeline_job_transformed_data with the value of prep_data.outputs.output_data
# Output 2: pipeline_job_trained_model with the value of train_model.outputs.model_output
return {
"pipeline_job_transformed_data": prep_data.outputs.output_data,
"pipeline_job_trained_model": train_model.outputs.model_output,
}
Step 2: To pass a registered data asset as pipeline job input, call function you created with data asset as input
from azure.ai.ml import Input
from azure.ai.ml.constants import AssetTypes
pipeline_job = pipeline_function_name(
Input(type=AssetTypes.URI_FILE,
path="azureml:data:1"
))
Step 3: Print the pipeline_job object created and review the YAML file created by running the @pipeline() function
print(pipeline_job) # printing the pipeline_job object you created
- Output will be YAML file including configuration of pipeline and its compoenents. Some parameters in YAML file are:
display_name: pipeline_function_name
type: pipeline
inputs:
pipeline_job_input:
type: uri_file
path: azureml:data:1
outputs:
pipeline_job_transformed_data: null
pipeline_job_trained_model: null
jobs:
prep_data:
type: command
inputs:
input_data:
path: $
outputs:
output_data: $
train_model:
type: command
inputs:
input_data:
path: $
outputs:
output_model: $
tags: {}
properties: {}
settings: {}
Run a Pipeline Job
Step 1: Configure a Pipeline Job
After creating pipeline by either using YAML file or @pipeline() function, pipeline configurations can be edited if needed:
- Changing Output mode for pipeline job outputs
# change the output mode pipeline_job.outputs.pipeline_job_transformed_data.mode = "upload" pipeline_job.outputs.pipeline_job_trained_model.mode = "upload" - Set default pipeline compute if not specified
# set pipeline level compute pipeline_job.settings.default_compute = "aml-cluster" - Change default datastore to where all outputs will be stored
# set pipeline level datastore pipeline_job.settings.default_datastore = "workspaceblobstore" - Review pipeline configuration by printing pipeline job object
print(pipeline_job)
Step 2: Run a pipeline job/Submit pipeline job
# submit job to workspace
pipeline_job = ml_client.jobs.create_or_update(
pipeline_job, experiment_name="pipeline_job"
)
After submitting, new job will be created. Pipeline job also contains child jobs, which represent execution of the individual components. Azure ML Studio creates graphical representation of pipeline.
Step 3: Schedule a Pipeline Job
To automate the retraining of a model, schedule a pipeline. There are various ways to create schedule.
- Create Time-based schedule using RecurrenceTrigger class
Sample schedule that fires every minute
from azure.ai.ml.entities import RecurrenceTrigger
schedule_name = "run_every_minute"
recurrence_trigger = RecurrenceTrigger(
frequency="minute", # Unit of time to describe how often the schedule fires. Value can be either minute, hour, day, week, or month.
interval=1, # Number of frequency units to describe how often the schedule fires. Value needs to be an integer.
)
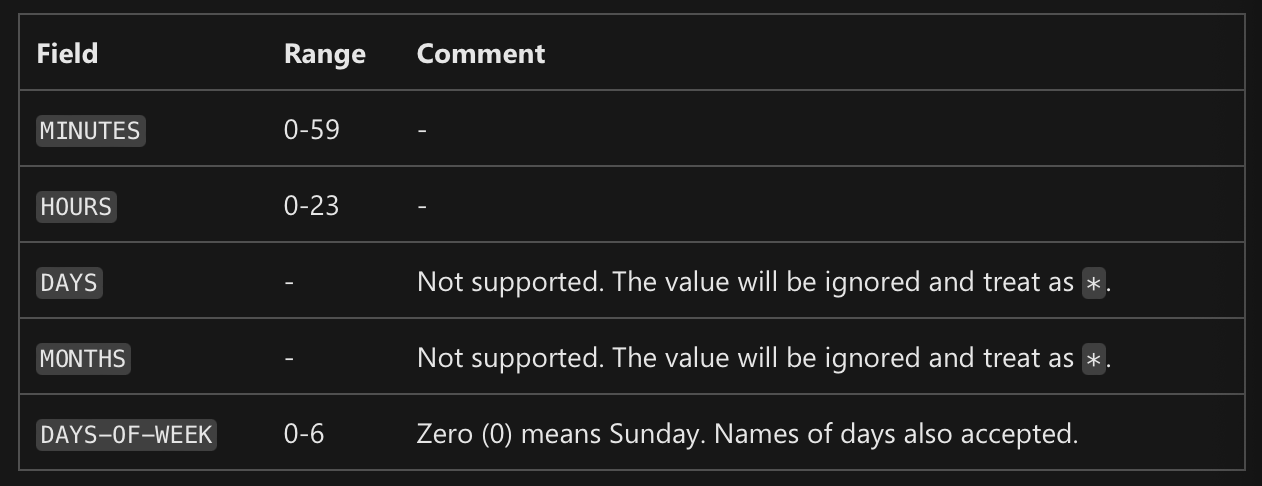
IMP NOTE: Create a time-based schedule with cron expression
schedule_name = "simple_sdk_create_schedule_cron" schedule_start_time = datetime.utcnow() cron_trigger = CronTrigger( expression="15 10 * * *", # Syntax: Minutes Hours Days Months Days-Of-Week start_time=schedule_start_time, # start time time_zone="Eastern Standard Time", # time zone of expression ) job_schedule = JobSchedule( name=schedule_name, trigger=cron_trigger, create_job=pipeline_job )
- Schedule pipeline using JobSchedule class
from azure.ai.ml.entities import JobSchedule
job_schedule = JobSchedule(
name=schedule_name, trigger=recurrence_trigger, create_job=pipeline_job
)
job_schedule = ml_client.schedules.begin_create_or_update(
schedule=job_schedule
).result()
- Delete schedule (Disable it)
ml_client.schedules.begin_disable(name=schedule_name).result()
ml_client.schedules.begin_delete(name=schedule_name).result()