Ksama Arora
Steps to Optimize Hyperparameters:
Step 1: Define Parameter Search Space:
- Specify batch size and number of hidden layers
{
"batch_size": choice(1, 2, 3, 4)
"number_of_hidden_layers": choice(range(1,5))
}
from azureml.train.hyperdrive import GridParameterSampling
from azureml.train.hyperdrive import choice
param_sampling = GridParameterSampling({
"num_hidden_layers": choice(1, 2, 3),
"batch_size": choice (16, 32)
}
)
Step 2: Specify Primary Metric:
- Choose a primary metric to optimize, such as accuracy.
primary_metric_name="accuracy",
primary_metric_goal=PrimaryMetricGoal.MAXIMIZE
Step 3: Specify Early Termination Policy:
- Select a policy to stop low-performing runs early.
from azureml.train.hyperdrive import BanditPolicy
early_termination_policy = BanditPolicy
(slack_factor = 0.1, evaluation_interval=1, delay_evaluation=5)
Step 4: Create and Assign Resources:
- Allocate computational resources for the experiment.
max_total_runs=20, max_concurrent_runs=4
Step 5: Launch Experiment:
- Run the experiment with the defined configuration.
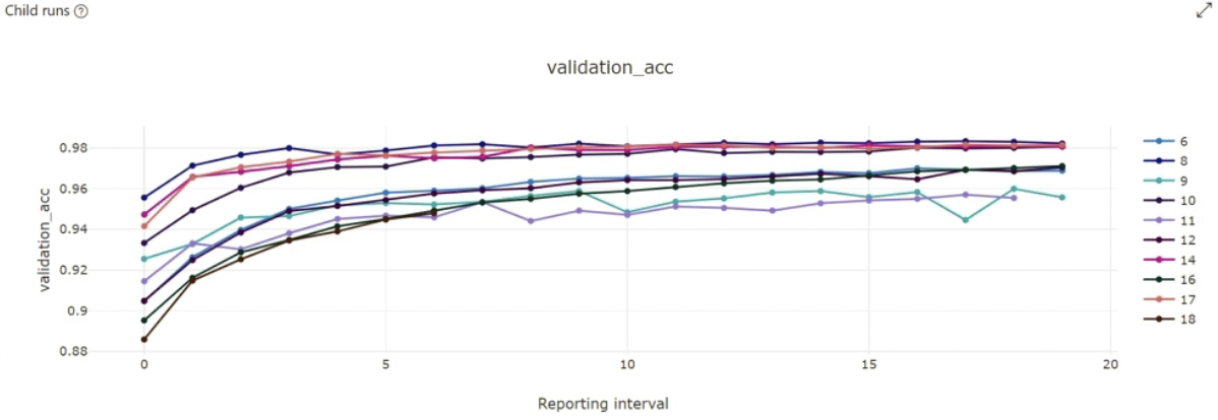
Step 6: Visualize Training Runs:
Step 7: Select Best Configuration:
- Choose the hyperparameter configuration that yields the best performance.