Ksama Arora
Run Training Script as Command Job in Azure Ml
Step 1: Convert a Notebook to a Script
Scripts are ideal for testing and automation in production. To create a production-ready script:
- Remove nonessential code: Exclude unnecessary code like print() and df.describe() (i.e. code for exploratory purposes) to reduce costs and compute time.
- Refactor into functions: Break down the code into smaller functions to test parts of the code independently resulting in run of only the required part of code.
Example notebook code to read and split data:
# read and visualize the data
print("Reading data...")
df = pd.read_csv('diabetes.csv')
df.head()
# split data
print("Splitting data...")
X, y = df[['Pregnancies','PlasmaGlucose','DiastolicBloodPressure','TricepsThickness','SerumInsulin','BMI','DiabetesPedigree','Age']].values, df['Diabetic'].values
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.30, random_state=0)
Refactored into two functions - Read the data & Split the data:
- Note: A script consisting of multiple functions is best to use for production workloads. E.g. A data scientist has trained a model in a notebook. The model should be retrained every week on new data.
# Import libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve
def main(csv_file):
df = get_data(csv_file)
# Split data
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = split_data(df)
# function that reads the data
def get_data(path):
df = pd.read_csv(path)
return df
# function that splits the data
def split_data(df):
X, y = df[['Pregnancies','PlasmaGlucose','DiastolicBloodPressure','TricepsThickness','SerumInsulin','BMI','DiabetesPedigree','Age']].values, df['Diabetic'].values
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.30, random_state=0)
return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
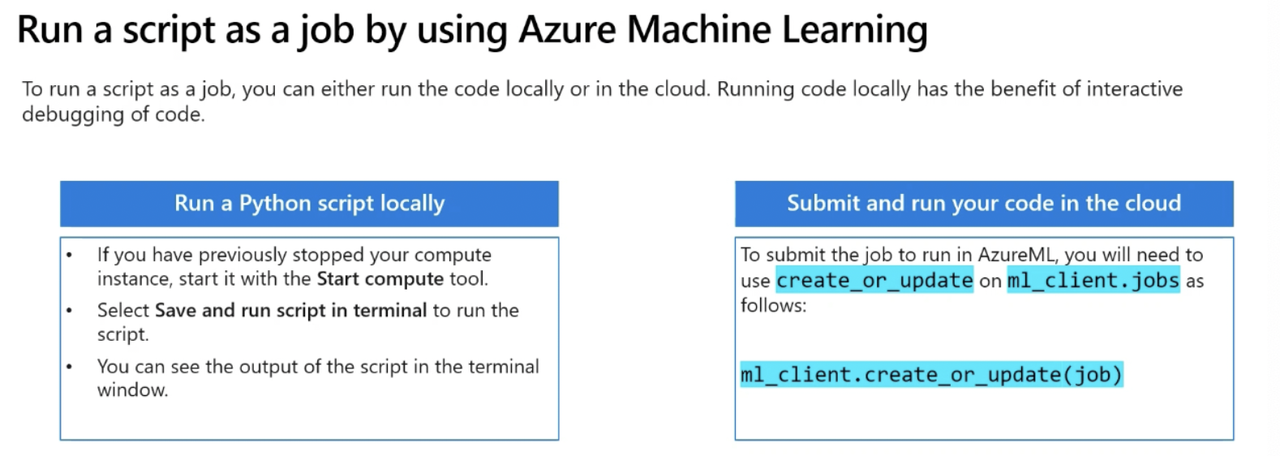
Test the script in the terminal:
- Open notebook page of Azure ML Studio -> save and run script in terminal
- OR
- Go to compute page -> select terminal of compute instance -> use command to run python script named train.py
python train.py
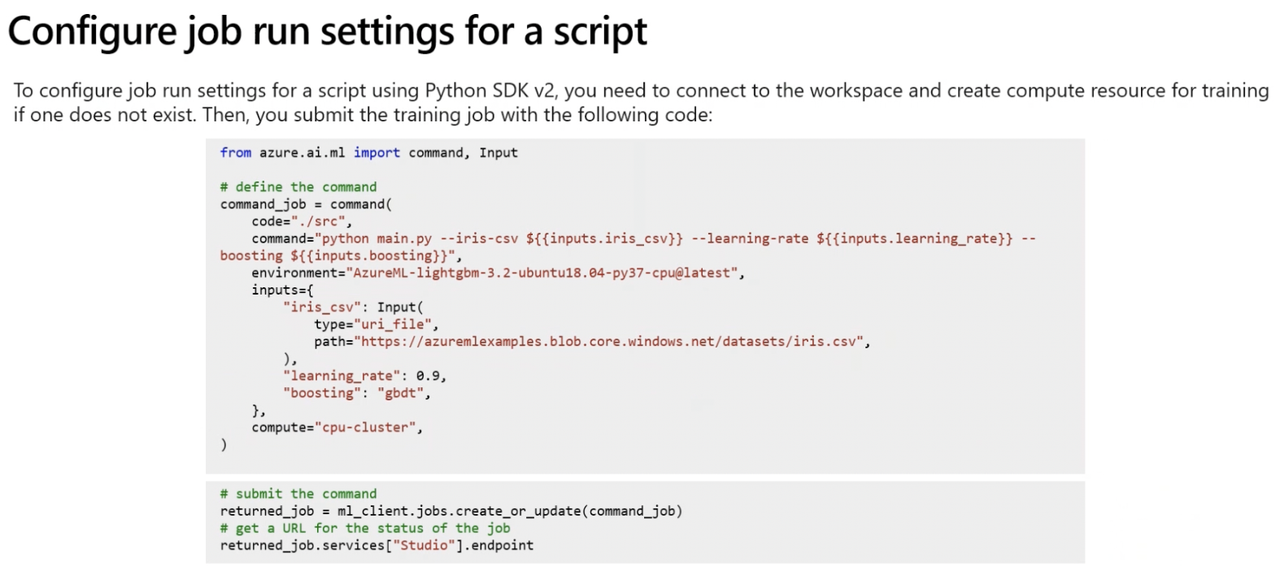
Step 2: Run a Script as a Command Job
from azure.ai.ml import command
# Configure job
job = command(
code="./src", # Folder containing the script
command="python train.py", # Specifies the file to run
environment="AzureML-sklearn-0.24-ubuntu18.04-py37-cpu@latest", # Required packages
compute="aml-cluster", # Compute resource
display_name="train-model", # Job name
experiment_name="train-classification-model" # Experiment name
)
# Submit job
returned_job = ml_client.create_or_update(job)
aml_url = returned_job.studio_url
print("Monitor your job at", aml_url)
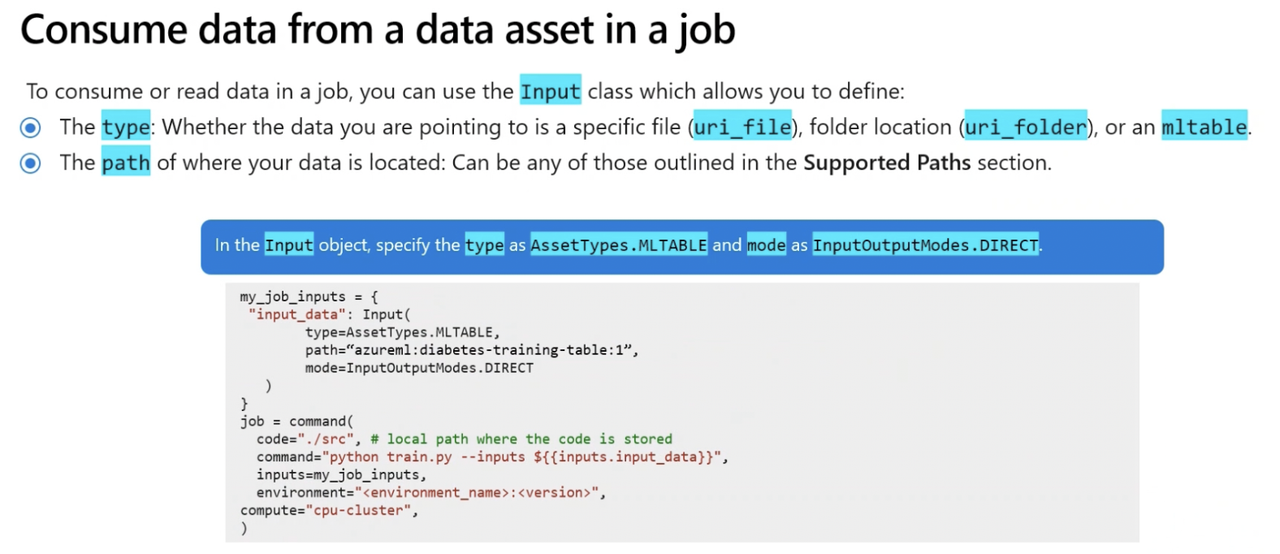
Step 3: Use Parameters in Command Job
Increase script flexibility using parameters.
Using script arguments:
import argparse # using library argparse
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
def main(args):
# read data
df = get_data(args.training_data)
# function that reads the data
def get_data(path):
df = pd.read_csv(path)
return df
def parse_args():
# setup arg parser
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
# add arguments
parser.add_argument("--training_data", dest='training_data', type=str)
# parse args
args = parser.parse_args()
# return args
return args
# run script
if __name__ == "__main__":
# parse args
args = parse_args()
# run main function
main(args)
Passing arguments to a script:
python train.py --training_data diabetes.csv
Configure command job with arguments:
from azure.ai.ml import command
job = command(
code="./src",
command="python train.py --training_data diabetes.csv",
environment="AzureML-sklearn-0.24-ubuntu18.04-py37-cpu@latest",
compute="aml-cluster",
display_name="train-model",
experiment_name="train-classification-model"
)